Breast Cancer, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor. Breast cancer occurs when breast cells become abnormal and are divided without control or sequence. Normal cells are divided and produced in sequence. Sometimes this sequential process is disrupted and cells grow and split out of control producing extra tissue that forms a period or a lump called a tumor. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancer). Breasts are mostly made of fat cells and gland cells. The milk-producing glands in the breast are made of individual cells that normally reproduce under the control of hormones. Sometimes this reproductive process is uncontrolled and abnormal glandular structures are formed. This is the beginning of cancer. The majority of breast cancer stems from milk ducts. A small part starts from a milk bag or lobule.
How common is Breast Cancer?
More than 20% of all cancers diagnosed in women are breast cancer. Between 2005 and 2009, about 1490 women were diagnosed with breast cancer in Singapore each year.Nine out of 10 women who go to doctors with breast lumps have benign lumps, not cancer. The normal changes associated with the menstrual cycle can make the breast feel lumpy.
Age Attack
The risk of breast cancer increases with age. Most women diagnosed with breast cancer are more than 40 years old, but younger women may also experience it.Causes and Risks Breast Cancer

Breast cancer is often triggered by the recurrence of the normal female hormone monthly cycle. The length of the fertile period, ie from the first period until menopause, is a risk factor. Women who are menopausal at age 55 are at significantly greater risk than menopauses at age 45. Age at first pregnancy is also important: the first pregnancy after the age of 30 years increases the risk compared with those with the first pregnancy before age 30. Likewise, women who have never been pregnant also have a higher risk. Breastfeeding also protects against breast cancer. Hormone replacement therapy increases the risk of breast cancer and this should be considered before starting treatment.
Between 5 to 10% of all breast cancers are associated with genetic factors. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have been identified and may be linked to breast cancer that occurs in about half of all families with a very strong history of breast cancer and/or ovarian cancer.
Breast Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms and Signs of Breast Cancer
About 80% of women with breast cancer first consult their physician with symptoms they find themselves. The most common form is a breast lump. The lump may be painful or may not. Sometimes the nipple may contract (pulled inward) or bleed, or there is a swelling of the breast skin. There may be fluid from the nipple. Axillary lymph nodes can also be enlarged. In advanced cases, breast cancer can spread to the liver, lung bone, or brain.
Read Also :symptoms of stage 1 breast-cancer
Breast Cancer Diagnosis
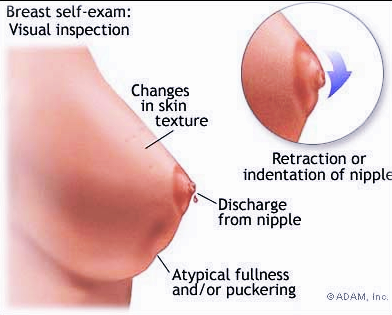
Diagnostic Test
Suspicious breast lumps are usually subject to X-rays called mammograms and needle biopsies. Even if a mammogram is negative, a biopsy may be necessary.
A mammogram is an x-ray examination that helps to determine the size of the lump. Sometimes it is combined with breast ultrasound to determine if the lump is mostly solid or cyst, which contains only fluids. The mammogram examination is slightly uncomfortable because the breast is pressed against the metal surface to get a good x-ray. Mammograms are much more useful for screening than for symptomatic period evaluation. Even if the mammogram is entirely normal, the symptomatic period of the breast may still need to be biopsied.
The biopsy involves removal of tissue from the breast lump using a needle or a thin core and injections. This can be done at the clinic. The tissue is processed and sent to the pathologist, the doctor will see the tissue under a microscope. The pathologist can tell whether the tissue is cancerous.
The mammotome breast biopsy is a new technology that uses vacuum-assisted devices to obtain biopsies from unexplained lesions. This tool can be guided by ultrasound or x-rays. Small tissue samples are removed from the breast using a hollow needle that is guided right into a suspicious lesion through a mammogram. This procedure is minimally invasive compared to open surgical biopsy and performed as an outpatient procedure. Mammotome has the ability to sample small abnormalities in X-ray, called microcalcifications, which allows early diagnosis of breast cancer. This is done under local anesthetic and takes about 45 minutes to complete.
Once the cancer is diagnosed, other tests such as chest x-ray, liver ultrasound, and bone scan may be needed to determine whether cancer has spread to other body parts.
Breast Cancer Treatment Options
Breast Cancer Treatment
Surgery is usually the first treatment for breast cancer. The desired goal of surgery is to maintain breasts whenever possible, and this involves removing cancer with the minimum number of the safest surrounding tissue (eg wide excision).
There are some patients where this is not possible and the total removal of the underlying breast and muscle, (ie the mastectomy), is required. Lymph nodes under the armpits can be removed entirely during surgery. (ie axillary cleansing) or, alternatively, the dye may be injected into the primary tumor area to determine the most informative single gland to remove (sentinel sampling mode). It's important to predict the likelihood of recurrent cancer.
Radiotherapy after surgery may be necessary if it is felt that there may be remnants of cancer cells in the remaining breast tissue that may cause breast cancer to grow again later in life (ie locally repeated). Radiotherapy in the chest usually takes 5 weeks. Radiotherapy is almost always recommended only if extensive excision of cancer is done.
Chemotherapy aims to prevent the recurrence of cancer in tissues that are distant from the breast. Chemotherapy is usually done in younger women and is given for 3 to 6 months. There may be mild nausea or vomiting, hair loss, lethargy or fatigue, and loss of appetite. Most women can continue to work during this period. The recommended choice of medication depends on one's general health and other medical problems, stage of cancer, and other risk factors.
Some breast cancers have specialized protein receptors in cancer cells, such as estrogen and progesterone receptors, and Her-2neu receptors. Patients with breast cancer have estrogen receptor or progesterone more benefit with additional hormone treatment. For patients with advanced breast cancer where cancer has a Her-2neu receptor, the antibody to Her-2neu has been developed for therapeutic purposes. Studies with Her-2neu antibodies are still ongoing: because of the possibility of heart damage, this therapy has not been considered standard therapy in an adj (propylene) setting.
Sometimes chemotherapy is given before surgery in order to minimize breast cancer before surgery. This usually occurs especially if the breast cancer is large.
In older women who have reached menopause, chemotherapy is not always necessary; only hormones such as tamoxifen may be needed. This is if the cancer receptor estrogen or progesterone positive.
Advanced Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can spread to the liver, liver, bone or brain, either at the time of diagnosis or many years after the breast cancer is removed. Treatment options include hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.Prognosis of Breast Cancer
Prognosis means the likelihood of future disease progression based on relevant facts in the case. All findings from clinical examination and investigation and pathology reports are important and should be considered together to decide the prognosis of individual cases of breast cancer.The doctor looks for the following features:
- The size of breast cancer is important. In general, the greater cancer, the more likely it is for recurrent cancer. The size of breast cancer also affects whether maintaining the breasts can be considered.
- How are many lymph nodes in the armpits involved? The more lymph nodes involved, the more likely it is that cancer recurs.
- Do pathologists look at high-risk features such as vascular or lymph node involvement in the specimens taken? Are cancer cells mature or not?




Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas, cancers that arise in glandular cells of the prostate’s epithelial tissue. Prostate cancers usually progress slowly and produce no symptoms in the initial stages. Eventually, the tumor may enlarge like mine use too, the prostate gland, pressing on the urethra and causing painful or frequent urination and blood in the urine. So I was so uncomfortable with this prostate cancer diseases then I decided to do online search on how to cure cancer because I well have read a lot about herbal medicine, I came across a lot of testimony how Dr Itua cure HIV/herpes then Cancer was listed below the comment.with courage I contacted Dr Itua and he sent me his herbal medicine through Courier service then I was asked to pick it up at my post office which i quickly did. I contacted Dr Itua that i have received my herbal medicine so he instructs me on how to drink it for three weeks and that is how Dr Itua Herbal Medicine cure my prostate Cancer, The treatment t…